Download A4Medicine Mobile App
Empower Your RCGP AKT Journey: Master the MCQs with Us!
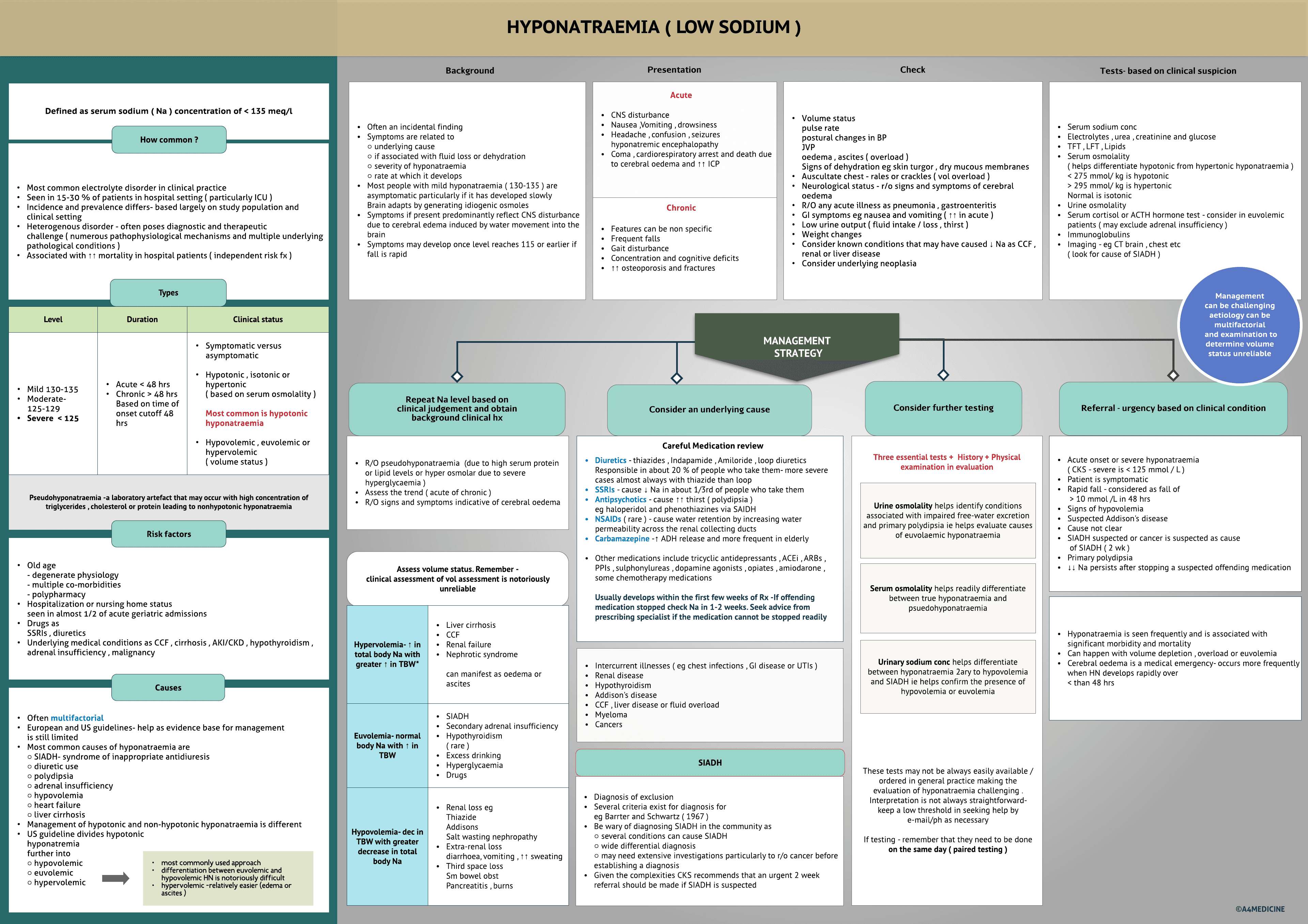
Hyponatraemia -Defined as serum sodium ( Na ) concentration of < 135 meq/l
Most common electrolyte disorder in clinical practice Seen in 15-30 % of patients in hospital setting ( particularly ICU ) Incidence and prevalence differs- based largely on study population and clinical setting Heterogenous disorder - often poses diagnostic and therapeutic challenge ( numerous pathophysiological mechanisms and multiple underlying pathological conditions ) Associated with ↑↑ mortality in hospital patients ( independent risk fx )
Mild 130-135 Moderate- 125-129 Severe < 125. Acute < 48 hrs Chronic > 48 hrsBased on time of onset cutoff 48 hrs. Symptomatic versus asymptomatic Hypotonic , isotonic or hypertonic ( based on serum osmolality )Most common is hypotonic hyponatraemia Hypovolemic , euvolemic or hypervolemic ( volume status )
Pseudohyponatraemia -a laboratory artefact that may occur with high conc of triglycerides , cholesterol or protein leading to nonhypotonic hyponatraemia
Risk factors- Old age- degenerate physiology- multiple co-morbidities- polypharmacy Hospitalization or nursing home statusseen in almost 1/2 of acute geriatric admissions Drugs asSSRIs , diuretics Underlying medical conditions as CCF , cirrhosis , AKI/CKD , hypothyroidism , adrenal insufficiency, malignancy
Often multifactorial European and US guidelines- help as evidence base for managementis still limited Most...
Try our Free Plan to get the full article.